What Is a Premium in Health Insurance? Explained Simply
In the world of health insurance, understanding the various costs and components of a plan is crucial to making informed decisions that protect both your health and your finances. One of the most commonly used and important terms you’ll encounter when shopping for or managing a health insurance policy is the premium. Simply put, a health insurance premium is the amount you pay—typically on a monthly basis—to keep your health insurance coverage active. This cost is paid whether or not you use healthcare services, and it acts as your membership fee to remain enrolled in your insurance plan.
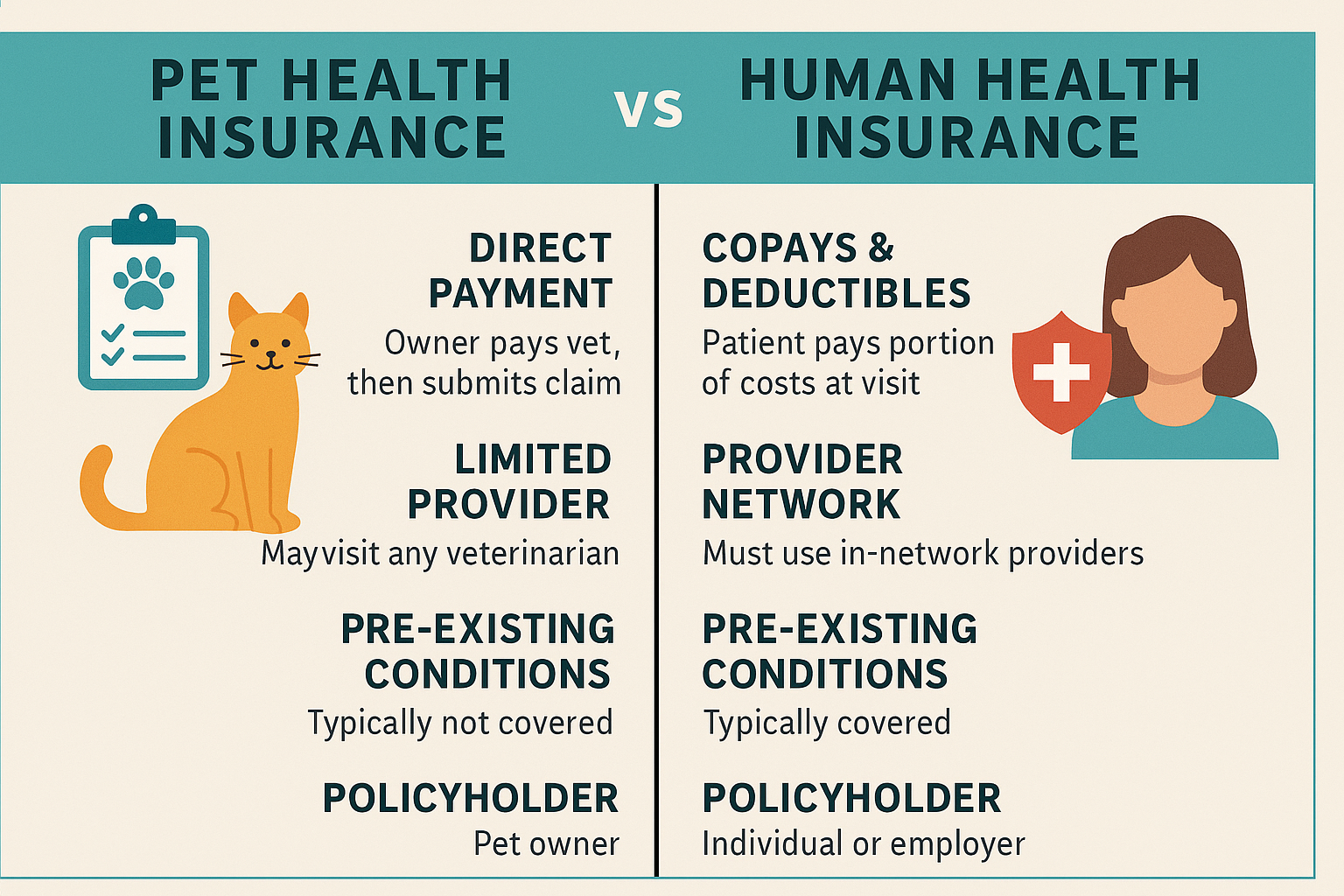
Health insurance premiums vary based on several key factors, including the type of plan you choose, your age, location, tobacco use, the number of people covered, and the level of coverage offered. Generally, plans that offer more comprehensive coverage and lower out-of-pocket costs will have higher premiums, while those with less coverage and higher deductibles tend to have lower monthly premiums. For example, a high-deductible health plan (HDHP) might offer a more affordable premium but could lead to higher costs when you actually receive care, since you’ll pay more out-of-pocket before the insurance company starts to share the cost.
Understanding how premiums fit into the broader cost structure of a health insurance plan is essential. In addition to the premium, you may also be responsible for other expenses such as deductibles, co-pays, co-insurance, and out-of-pocket maximums. However, the premium is the foundational cost that keeps your plan active, and if it is not paid on time, you risk losing your coverage. Many insurers offer grace periods or automatic payment setups to help policyholders stay current, but missing payments can result in canceled coverage and significant financial risk if unexpected health issues arise during a lapse.
Premiums are not just a number—they reflect the value and stability of your health coverage. For individuals and families, the challenge lies in finding a balance between a premium that fits within your budget and a plan that offers the medical services and financial protection you need. Subsidies and tax credits available through government marketplaces can help lower premiums for eligible individuals, making health coverage more accessible and affordable. These financial assistance options are especially beneficial for low- to middle-income households and should be explored during the open enrollment period each year.
When evaluating health insurance plans, it’s important not to focus solely on the premium. While a lower premium might seem attractive, it could be offset by higher deductibles and limited provider networks. Conversely, a higher premium might be justified if it provides access to a broader range of doctors, better prescription coverage, and more predictable out-of-pocket costs. The key is to compare all aspects of the plan, including premium, benefits, network, and your personal healthcare needs, to determine the best fit.
In summary, the premium is a fundamental part of your health insurance plan—it is the monthly price you pay to ensure you and your family have access to healthcare services when needed. By understanding what a premium is, how it works, and how it interacts with other plan costs, you can make smarter, more confident choices during enrollment periods. Always consider your health habits, financial situation, and the total cost of care—not just the monthly premium—to find a plan that truly meets your needs. Whether through employer-sponsored insurance, government programs, or private marketplaces, being informed about premiums puts you one step closer to achieving financial and physical well-being.